Other Earth Observing Satellites
In addition to the Landsat program, there are many additional Earth Observing Satellites. We will cover some of the more significant earth observing satellites in this section.
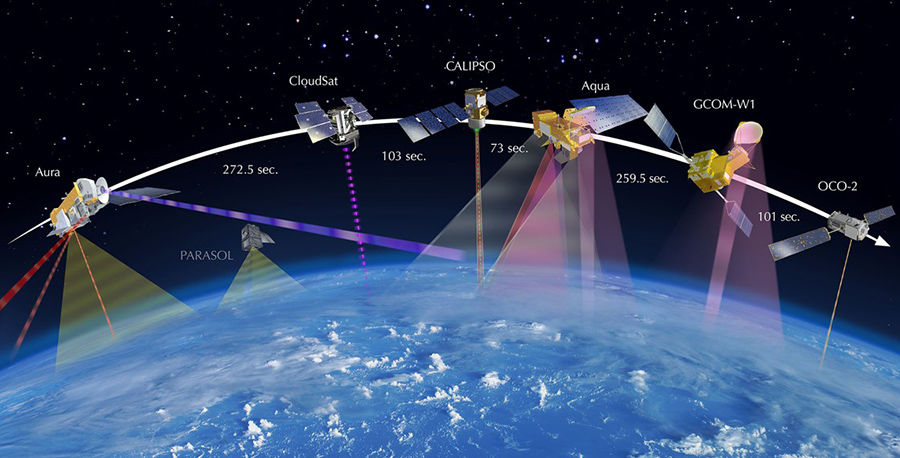
The Afternoon Constellation
NASA and its international partners operate several Earth-observing satellites that closely follow one after another along the same orbital “track.” This coordinated group of satellites is called the Afternoon Constellation, or the A-Train, for short. The satellites are in a polar orbit, and cross the equator at about 1:30 pm, within minutes of each other. This produces near-simultaneous observations of a wide variety of parameters to aid the scientific community in advancing our knowledge of Earth-system science and applying this knowledge for the benefit of society.
Aqua & Terra Satellites
Terra was launched in 1999 and is the flagship of the Earth Observing System. It is designed to monitor the state of Earth's environment and changes in its climate system. It has a sun-synchronous orbit, meaning it crosses over the equator at approximately the same local time each day. Terra has a total of five sensors on the satellite. Aqua is part of the A-Train and was launched in 2002 as the "sister” satellite to Terra. It is designed to monitor studying the precipitation, evaporation, and cycling of water and like Terra, it has a sun-synchronous orbit and five sensors.
| Sensors on Aqua | Sensors on Terra |
|---|---|
|
|
Moderate-resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS)

Phytoplankton bloom in the Bering Sea, MODIS:Terra Satellite September 26th, 2014
Moderate-resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) is a sensor that is located on both the Terra and Aqua satellites. Terra's orbit around the Earth is timed so that it passes from north to south across the equator in the morning, while Aqua passes south to north over the equator in the afternoon. Terra MODIS and Aqua MODIS view the entire Earth's surface every 1 to 2 days, producing up-to-date imagery. MODIS has 36 spectral bands ranging in wavelength from 0.4 µm to 14.4 µm and varying spatial resolutions (2 bands at 250 m, 5 bands at 500 m and 29 bands at 1 km). While MODIS does not have extremely high spatial resolution, it does have high temporal and spectral resolution.
Advanced Spaceborne Thermal Emission and Reflection Radiometer (ASTER)
The Advanced Spaceborne Thermal Emission and Reflection Radiometer (ASTER) is an imaging instrument onboard Terra. ASTER captures high spatial resolution data in 14 bands, from the visible to the thermal infrared wavelengths, and provides stereo viewing capability for digital elevation model creation. ASTER is the only high spatial resolution instrument on the Terra platform. One thing that makes ASTER unique is its point-able sensor. This ‘zoom’ lens is particularly important for change detection, calibration/validation and land surface studies. Unlike the other instruments aboard Terra, ASTER does not collect data continuously; rather, it collects an average of 8 minutes of data per orbit.
Sentinel-2
The Sentinel-2 mission consists of two satellites developed to support vegetation, land cover, and environmental monitoring. The Sentinel-2A satellite was launched by European Space Agency (ESA) on June 23, 2015, and operates in a sun-synchronous orbit with a 10-day return time. A second identical satellite (Sentinel-2B) was launched March 7, 2017. Together they cover all Earth’s land surfaces every five days. A partnership established between the ESA and the USGS allows for USGS storage and redistribution of data acquired by the multispectral instrument (MSI) on the European Union's Sentinel satellites. The MSI sensor acquires 13 spectral bands with varying spatial resolution (10m, 20m, 60m). View the full list of bands and wavelengths.
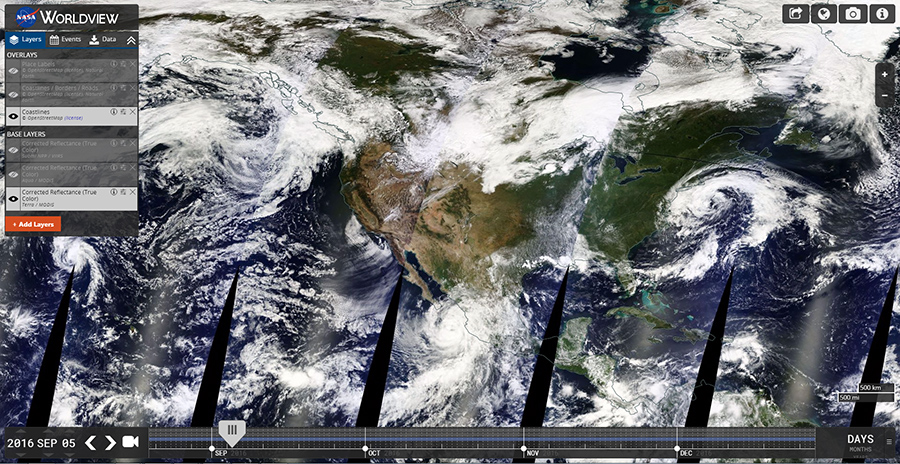
Explore: NASA Worldview
The Worldview tool from NASA's Earth Observing System Data and Information System (EOSDIS) provides the capability to interactively browse and download global, full-resolution satellite imagery. There are over 400 data products available to view and download. Most of the data products are updated within three hours of observation, providing nearly real-time imagery and data. Worldview also allows you to take and export high resolution screeshots and create animations of imagery overtime.