Spatial Statistics
Spatial Statistics can be used to explorer, compare and model data based on the spatial distribution, patterns and relationships. These tools can be used to tools for analyzing data distributions and patterns in the context of both space and time (temporally).
Zonal Tools (ArcMap)
The Zonal toolset in ArcMap allows you to perform analysis on data in certain zones or specific locations. A zone can be defined as being one single area of a particular value, but it can also be composed of multiple disconnected elements, or regions, all having the same value. Zones can be defined by raster or vector datasets. Rasters must be of integer type, and features must have an integer or string attribute field.
Zonal Statistics
The Zonal Statistics tool, a statistic(for example, min, mean max value etc.) is calculated for each zone defined by a dataset, based on values from another dataset (known as a value raster). The input zones can be from either vector or raster datasets. If the zone input is a raster dataset, the data must be integers and it must have an attribute table. The attribute table is usually created automatically for integer rasters, but may not be under certain circumstances. A single output value is computed for every zone in the input zone dataset. The Zonal Statistic tool creates an output raster displaying the results.
The Zonal Statistics as Table tool calculates all, a subset or a single statistic that is for the specific input but returns the result as a table instead of an output raster.
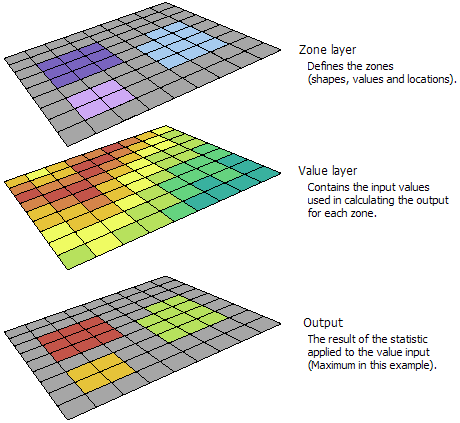 Example inputs and output from Zonal Statistics tool. Note that the zone layer can either be a vector file (feature dataset) or raster.
Example inputs and output from Zonal Statistics tool. Note that the zone layer can either be a vector file (feature dataset) or raster.
For the Zonal Statistics output, the output data type is determined by both the selected statistic type and the value input type. The following table identifies the statistics that can be calculated with these tools:
- Mean: Calculates the average of all cells in the value raster that belong to the same zone as the output cell.
- Majority: Determines the value that occurs most often of all cells in the value raster that belong to the same zone as the output cell.
- Maximum: Determines the largest value of all cells in the value raster that belong to the same zone as the output cell.
- Median: Determines the median value of all cells in the value raster that belong to the same zone as the output cell.
- Minimum: Determines the smallest value of all cells in the value raster that belong to the same zone as the output cell.
- Minority: Determines the value that occurs least often of all cells in the value raster that belong to the same zone as the output cell
- Range: Calculates the difference between the largest and smallest value of all cells in the value raster that belong to the same zone as the output cell.
- Standard deviation: Calculates the standard deviation of all cells in the value raster that belong to the same zone as the output cell.
- Sum: Calculates the total value of all cells in the value raster that belong to the same zone as the output cell.
Zonal Histogram
The Zonal Histogram Tool produces a table with the count of specific cell values in the input file within each unique zone. Similar to the Zonal Statistics tools, the input zones can be derived from vector files or from raster files. A zone is defined as all areas in the input that have the same value. The areas do not have to be contiguous. Essentially this tool enables you to investigate the frequency distribution of values in one dataset within classes of another dataset. Examples include slope distribution within land use classes, rainfall distribution within elevation classes, or crime distribution by police beat. A zonal histogram graph is not generated by default. To have it be created when the tool is run, specify the Output graph name.
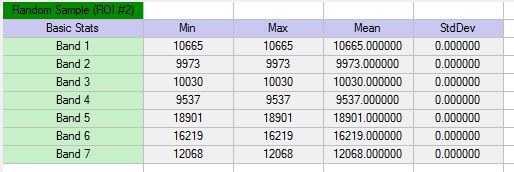
Statistics in ENVI
The Quick Stats tool in ENVI computes the basic statistics and histograms for all bands of a dataset. ENVI calculates the statistics and displays them in the Statistics View. In ENVI you can also compute pixel count (frequency) and percentage per class, basic statistics, and histograms for all bands on classified rasters (including classification images, Raster Color Slices, and Scatter Plot classes). These statistics can be exported as a text file for additional analysis.Statistics can also be computed and displayed for specific or all regions of interest (ROIs) wihtin a dataset.