Below are terms used with attributes in common GIS software:
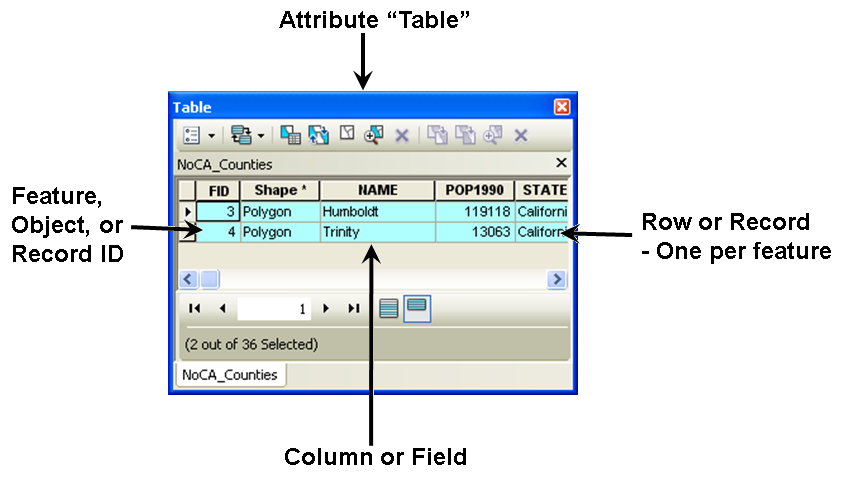
Each row in the attribute table corresponds to a single "feature" on the ground. Each column in the table is for a specific type of "attribute" for all the features in the file.
The terminology here can be a little confusing as ESRI borrows the terms for attributes from four different disciplines. This is because of some history where the attribute table is actually stored in a "DBase" (dbf) file. DBase was a database and we still use a database language (SQL) to query attributes. The spreadsheet terminology came along because we also import attributes from spreadsheets and more folks work with spreadsheets than databases. Object oriented programming (OOP) was a late addition and you can largely ignore it for attributes.
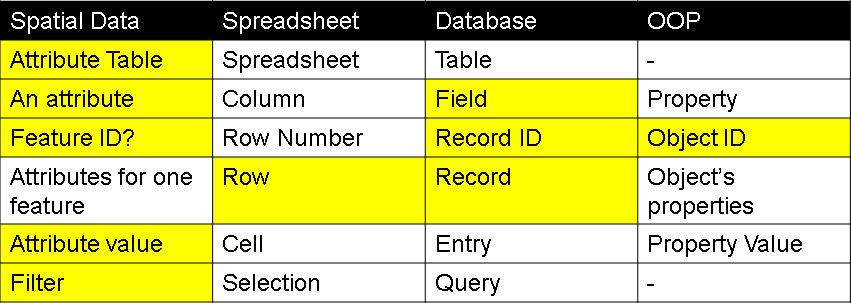
The terms shown in yellow are the ones used the most commonly used and you'll definitely want to know the meaning of: Field, Row, Attribute Table, Feature, and Filter.
It's common to find Attributes within vector data, an rare to find them with raster data. Some examples of attributes are:
What attributes might you want for the following layers for the HSU campus?
Vector Attributes are used for labels, symbology, selection, and sub-setting.
Some examples of Labels are:
Symbology:
Selection:
Sub-setting:
© Copyright 2018 HSU - All rights reserved.