Buffering creates polygons around existing vector features. You can access the Buffer Tool by navigating to ArcToolbox, Analysis, Proximity, and then Buffer.

Visit the interactive buffer page to learn more about buffers.
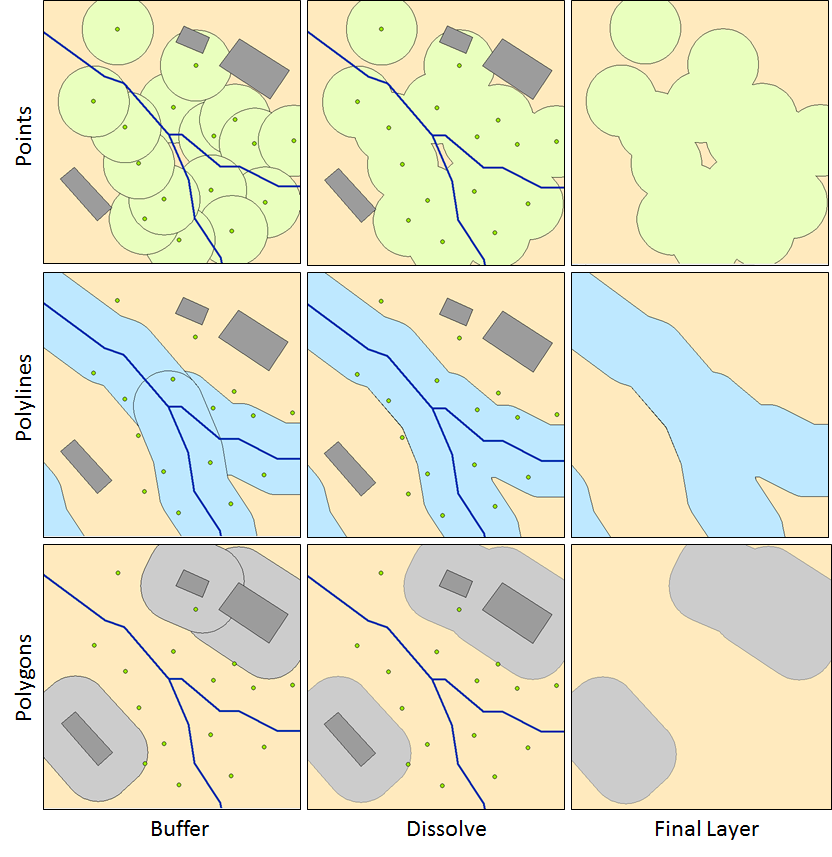
Buffer and dissolve work together in ArcMap. Below is an example with a stream (lines), some buildings (polygons), and trees (points).

The images below show the effect of buffer and dissolve on points, polylines, and polygons.
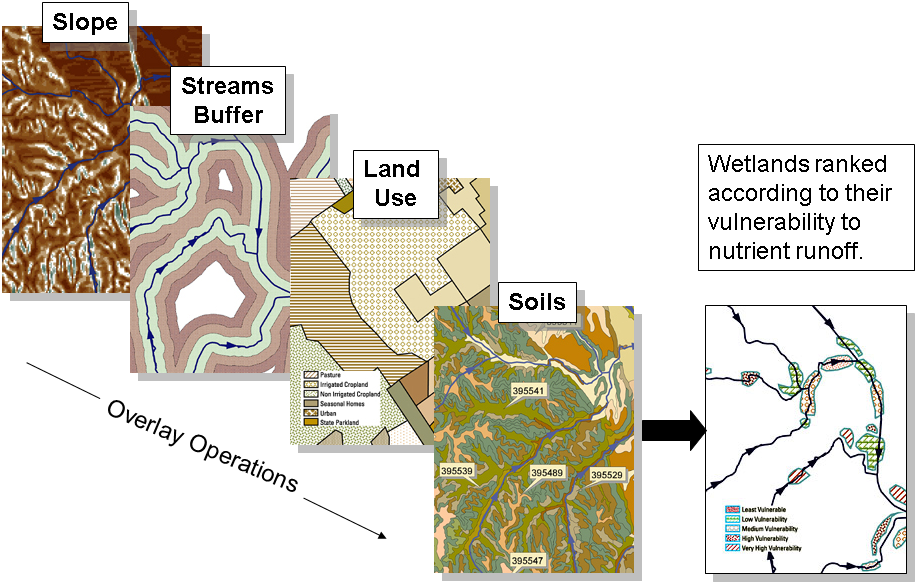
Overlay is the combination of separate data layers to derive new information (a new layer). Both spatial and (sometimes) attribute data are combined. The most common overlay operations are "Union" and "Intersection".

Play with the interactive overlay tool to get a feel for how overlay operations work and then continue with the commonly used overlay tools below.
The Intersect tool finds the intersection of features between two or more layers.

The Intersect Tool in ArcGIS performs an intersection and maintains the attributes for both intersecting features.

The Clip tool "clips" one layer with all the features from another. This is another type of intersection.

The Clip Tool only maintains the attributes for the original layer.
The Union tool combines the features from one or more layers into a single layer. The resulting features are the unique areas between the two layers (not a true Union).

Esri does not use this for the term "union."
This is actually clipping each feature to the bounds of every feature that overlaps with it. The resulting data set contains all the areas of the input layers with attributes attached for each feature that overlaps with each unique area. This is not really a union operation but instead merges two layers together and finds the unique areas of overlap.

This tool dissolves features in a layer together, which can be based on a common attribute value or all features together. This is a proper union.

The Erase tool uses one layer to "erase" area from another layer.

© Copyright 2018 HSU - All rights reserved.