There are a number of problems we can into with raster data.
Because of the large number of file formats available, fixing problems with spatial references with rasters can be more tricky than with vector data. In addition, a raster is just a rectangular grid of pixels so it must have additional information that "pins" that data to the earth (georeference it).
Missing or Incorrect Spatial References
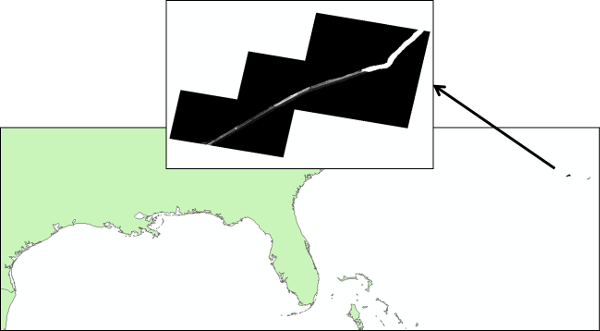
The signs that a raster is missing a spatial reference or that the spatial reference is incorrect is the same as for shapefiles. ArcGIS will alert you if the spatial reference is missing and you can check the spatial reference in "Properties". If the spatial reference is incorrect, the raster will not appear where it should. Below is an image of a raster with elevation data along the coast of the Gulf of Mexico that I downloaded from a government agency. the data appeared closer to the Bahamas than the Gulf of Mexico!
The challenge with rasters is that this could be because of an incorrect spatial reference or incorrect georeferencing. I had to spend some time with the raster trying different spatial references and discovered that is was an incorrect spatial reference. This meant I had to "define" the spatial reference to the correct one.
Rasters are always rectangular but quite often we want to "mask" part of the raster because the area of interest, or the area that actually have read data for, is smaller than the size of the raster. The raster below contains bathymetry (depth of the sea bed below the water level) for the Gulf of Mexico (in black and white) and the habitat for adult brown shrimp (in red). The raster in the background represents the entire raster and you can see there are black pixels in the upper left that just contain 0s and should definitely be "masked out". Most of the white area is land and is also in correct and should be masked out. What we have done is masked out everything but the area that we are interested in (habitat for adult brown shrimp) and colored it red.
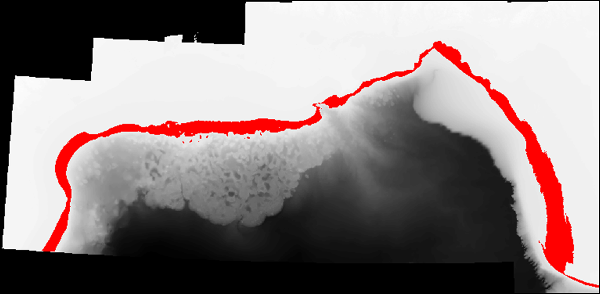
Esri refers to pixels that are "masked out" as "NoData" (properties and symbology) and sometimes as "NULL" values (in raster calculator). Sometimes when you bring a raster into ArcGIS you'll see that the range of values is crazy and it's hard to see your raster data. This is often because the NoData value was not specified in a way that ArcMap understands. You can use the "SetNull()" function in Raster Calculator to set areas that should be masked to NoData.
No data areas will not be used in calculations and statistics.
© Copyright 2018 HSU - All rights reserved.