Electromagnetic Radiation and Electromagnetic Spectrum
Introduction
In this lab we will become more familiar with electromagnetic radiation, how it is measured and its implications in remote sensing.
Learning Outcomes
- Become familiar with the relationship between wavelength, frequency and energy
- Understand wave theory, particle theory, Stefan-Boltzman law and Wein’s displacement law.
- Understanding the implications of electromagnetic radiation principles in the application of remote sensing
- Develop a working knowledge of the regions of the electromagnetic spectrum
Electromagnetic Radiation
Energy is a measure of the ability to do work and it comes in two main forms, kinetic (objects in motion), potential (stored energy like battereis). Electromagnetic energy is produced is a type of kinetic energy produced by the oscillating electric and magnetic disturbance, or by the movement of electrically charged particles.
Law of Conservation of Energy
The Law of Conservation of Energy states that energy can be transferred but not created or destroyed. Energy can be transferred in one of three ways:
- Conduction – transfer by physical contact
- Convection – transfer by movement
- Radiation – transfer of energy without the need of a medium
Electromagnetic energy transferred by radiation is known a electromagnetic radiation or EMR. EMR is the only energy that can travel through a vacuum – i.e. interstellar space. Light, electromagnetic waves, and radiation all refer to the same physical phenomenon: electromagnetic energy. All objects warmer than absolute zero (-273° C) emit Electromagnetic Radiation (EMR). Objects also reflect and absorb EMR emitted by other objects. The sun is a major source of electromagnetic radiation, emitting energy across several regions of the spectrum. All of this is key to remote sensing because Earth's surfaces refelct the sun's electromagnetic energy in unique ways.
Describing Elecromagnetic Energy
Frequency
Wavelength
energy
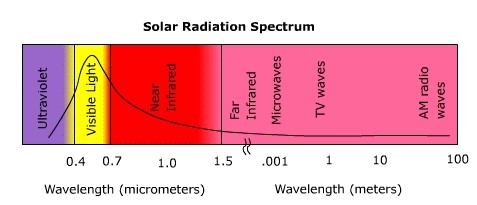
Electromagnetic Spectrum
The most familiar form of electromagnetic radiation is visible lightConverting from "Normal" to Scientific Notation
Converting from Scientific Notation to "Normal"
With Numbers from Scientific Notation
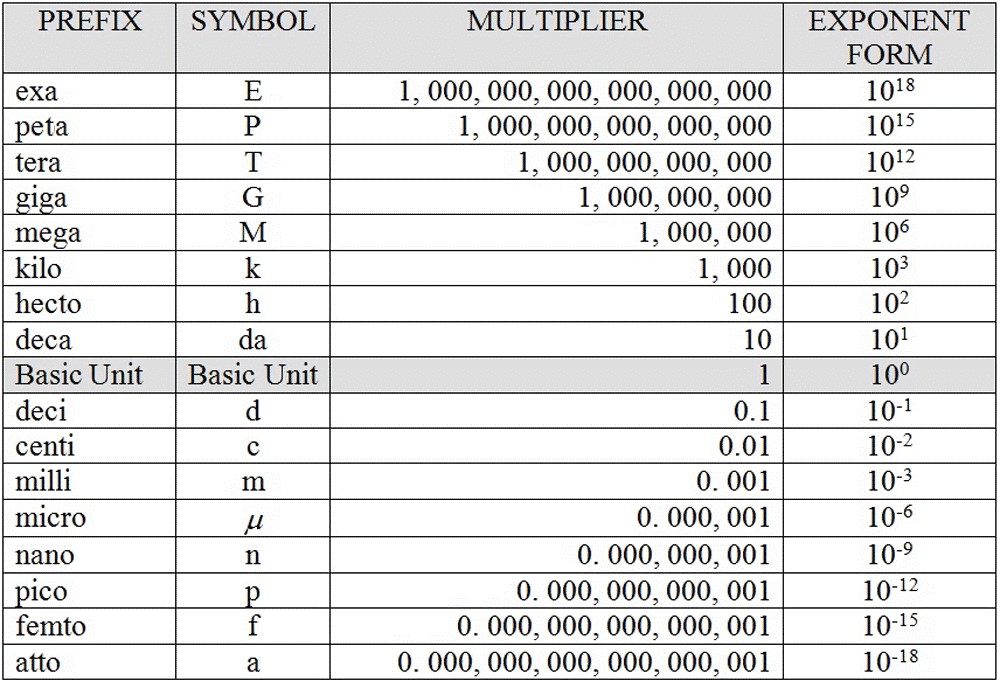
Metric Prefixes and Conversions
In addition to the use of scientific notation, you will also see a variety of metric prefixes used to describe wavelength and frequency.